Single-copy expression of an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked TDP-43 mutation (M337V) in BAC transgenic mice leads to altered stress granule dynamics and progressive motor dysfunction
Abstract
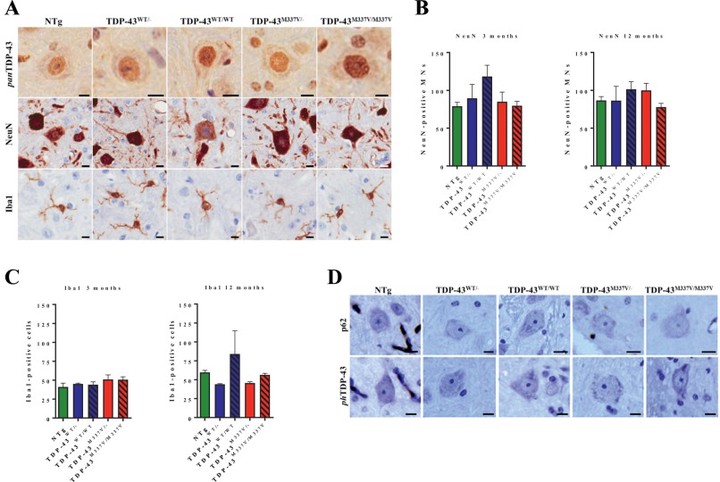
Mutations in the gene encoding the RNA-binding protein TDP-43 cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), clinically and pathologically indistinguishable from the majority of ‘sporadic’ cases of ALS, establishing altered TDP-43 function and distribution as a primary mechanism of neurodegeneration. Transgenic mouse models in which TDP-43 is overexpressed only partially recapitulate the key cellular pathology of human ALS, but may also lead to non-specific toxicity. To avoid the potentially confounding effects of overexpression, and to maintain regulated spatio-temporal and cell-specific expression, we generated mice in which an 80 kb genomic fragment containing the intact human TDP-43 locus (either TDP-43WT or TDP-43M337V) and its regulatory regions was integrated into the Rosa26 (Gt(ROSA26)Sor) locus in a single copy. At 3 months of age, TDP-43M337V mice are phenotypically normal but by around 6 months develop progressive motor function deficits associated with loss of neuromuscular junction integrity, leading to a reduced lifespan. RNA sequencing shows that widespread mis-splicing is absent prior to the development of a motor phenotype, though differential expression analysis reveals a distinct transcriptional profile in pre-symptomatic TDP-43M337V spinal cords. Despite the presence of clear motor abnormalities, there was no evidence of TDP-43 cytoplasmic aggregation in vivo at any timepoint. In primary embryonic spinal motor neurons and in embryonic stem cell (ESC)-derived motor neurons, mutant TDP-43 undergoes cytoplasmic mislocalisation, and is associated with altered stress granule assembly and dynamics. Overall, this mouse model provides evidence that ALS may arise through acquired TDP-43 toxicity associated with defective stress granule function. The normal phenotype until 6 months of age can facilitate the study of early pathways underlying ALS.